What is a Security Vulnerability? (Definition, Types, and Remediation)
All businesses have cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
And as a business owner, how are you dealing with these security vulnerabilities?
Do you scan for them? How often do you do it? Do you rank the vulnerabilities in order of criticality, from the most to least significant? Do you address them in that exact order?
At Intelligent Technical Solutions (ITS), we’ve been helping hundreds of businesses strengthen their network defenses for nearly two decades. One effective way to do that is by identifying vulnerabilities and addressing each before it develops into a security incident.
For this article, we’ve reached out to Jeff Farr, ITS Security Consultant, to discuss and answer the following questions:
- What is a security vulnerability?
- What are the types of security vulnerabilities?
- How can businesses identify these vulnerabilities?
- How often should vulnerability scans be done?
- How can businesses remediate these vulnerabilities?
After reading, you can bring to light security vulnerabilities in your computer systems, software applications, and procedures and resolve them immediately.
What is a security vulnerability?
Security vulnerabilities are flaws and weaknesses in an information system, whether they’re security procedures, internal controls, or exploitable implementation. It could be:
- An outdated software,
- A vulnerable system, or
- Anything in the network left unsupervised or unprotected.
These vulnerabilities are opportunities for bad actors to actualize their attacks.
Security Vulnerability vs. Security Incident
Once hackers are successful, the vulnerabilities turn into a security incident. A security incident means a potential breach has occurred and that your organization’s data and systems are compromised.
Farr gives a simple analogy of a house with unlocked doors and opened windows. Although these are not an invitation for burglars to come in, leaving it open already puts you at risk of a possible intrusion. That’s vulnerability. When the possibility turns into reality, an actual break-in happens, and they steal essential things from your house; that’s an incident.
“A security vulnerability means that you’re susceptible to a crime. An incident means that a crime has already occurred,” Farr said.
What are the types of security vulnerabilities?
Knowing how to remediate vulnerabilities in your business network helps to recognize what type you are dealing with. Here are a few classifications for a vulnerability:
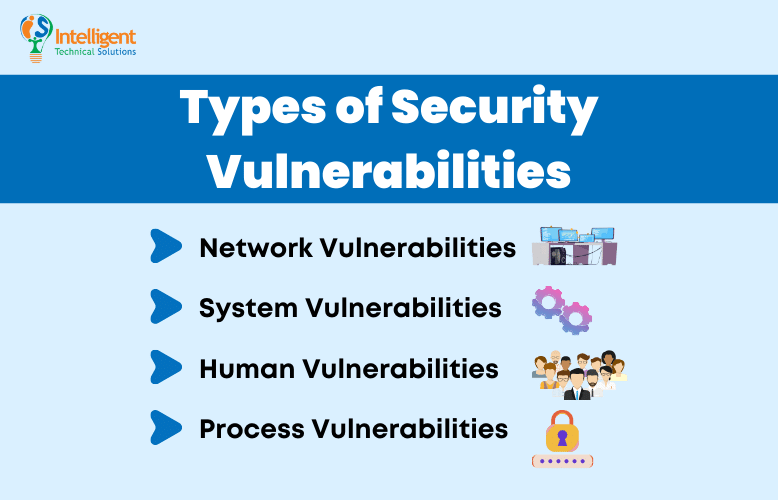
Network Vulnerabilities
These are issues with a network’s hardware or software that can expose it to possible intrusion by an outside party. Examples may include insecure Wi-Fi access points and poorly configured firewalls.
System Vulnerabilities
These are vulnerabilities within a particular operating system (OS) that hackers may exploit. They use this type of vulnerability to access or damage an asset where the OS is installed. Examples include default superuser accounts that may exist in some OS installations and hidden backdoor programs.
Human Vulnerabilities
The weakest link in many cybersecurity architectures is the team members. And while it’s understandable for humans to make mistakes, these errors can easily expose sensitive data, create exploitable access points for attackers, or disrupt systems.
Process Vulnerabilities
Some vulnerabilities can be created by specific process controls (or a lack thereof). One example would be the use of weak passwords, which may also fall under human vulnerabilities.
However, Farr says that knowing the types isn’t the main concern; you should care more about handling the most critical vulnerability first.
How can businesses identify security vulnerabilities?
According to Farr, the first step in managing risks is vulnerability scanning.
It is an inspection of the potential points of exploitation on a network to find security holes using a third-party application. A vulnerability scan detects and classifies system weaknesses in computers, networks, and communications equipment and predicts the effectiveness of countermeasures.
How often should vulnerability scans be done?
The effectiveness of this method depends on how often you scan. Some companies only scan for vulnerabilities once a year, others quarterly or monthly. While there is no recommended interval for vulnerability scans, Farr says that the more often you do it, the better.
Here’s why:
If you’ve had a vulnerability in January but don’t detect it until May, an incident may have already happened, and it’s already too late for you to salvage your data. But when you scan frequently, you narrow the window that somebody could get in and use the vulnerability to attack.
How can businesses remediate these vulnerabilities?
Just because you know that the front door is open doesn’t mean that burglars are out of the way. You must not only scan for these vulnerabilities, but you must fix them. Remember that the end game of vulnerability management is remediation.
According to Edgescan, the average time to remediate internet-facing vulnerabilities is 57.5 days. If you don’t act fast, this may even increase in numbers. That means more risks to your network and presumed extended downtime.
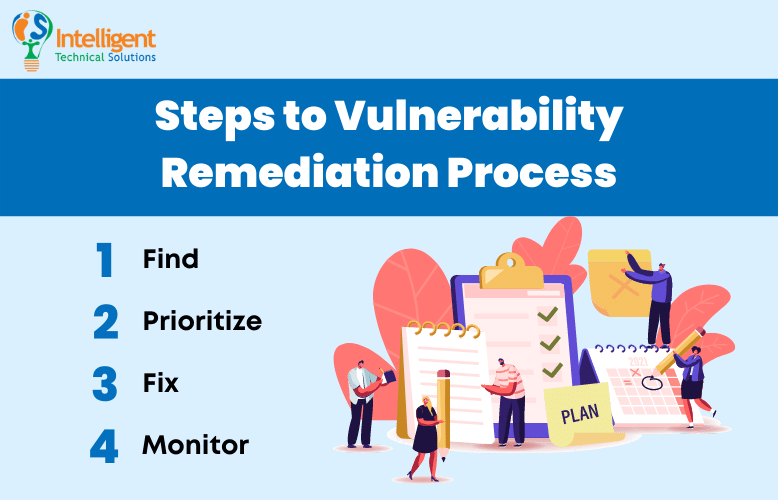
If you don’t want that to happen, here are the four steps to the vulnerability remediation process you must know now:
- Find. This is where you detect vulnerabilities through testing or vulnerability scanning, as discussed in the previous paragraphs.
- Prioritize. After finding the vulnerabilities, you must understand which vulnerabilities pose a real and significant risk. That would be what you need to prioritize when doing the third step.
- Fix. Here is where you patch and block or otherwise fix vulnerabilities at scale and in real time.
- Monitor. Finally, you must continuously monitor projects and code for newly discovered vulnerabilities, with real-time alerts and notifications via all the relevant channels.
Need help managing your security vulnerabilities?
Cybersecurity is critical for your business to thrive. Thus, protecting your network from known and unknown vulnerabilities is essential. As a recap, here are the types of security vulnerabilities you must know:
- Network
- System
- Human
- Process
And here are the steps to remediate the risks:
- Find the vulnerabilities
- Prioritize the levels of criticality
- Fix the issues found
- Monitor continuously
ITS is committed to helping you find the right security solutions to your problems. As you find and fix the vulnerabilities in your network, you may bolster your network defenses proactively. Read our e-book on the three types of cybersecurity solutions your business must have.



